Jinan University
Guangzhou,Guangdong Province
Guangzhou, traditionally romanised as Canton, is the capital and largest city of the Province of Guangdong in southeastern China. Guangzhou is, at the moment, the 3rd-largest Chinese city, behind Beijing and Shanghai; holds sub-provincial administrative status; and is one of China's five National Central Cities. In 2015 the city's administrative area was estimated to have a population of 13,501,100 and forms part of one of the most populous metropolitan agglomerations on Earth.
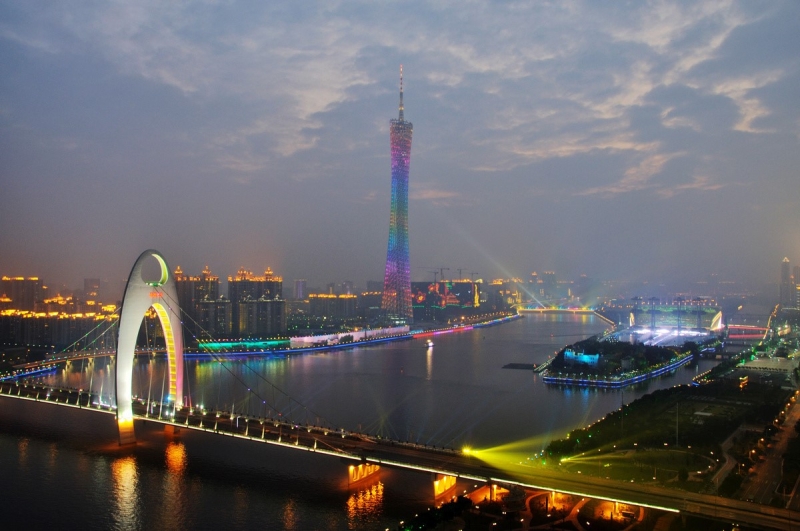

Geography
Located on the Pearl River about 120 km (75 mi) north-northwest of Hong Kong and 145 km (90 mi) north of Macau, Guangzhou was a major terminus of the maritime Silk Road and continues to serve as a major port and transportation hub. Located just south of the Tropic of Cancer, Guangzhou has a humid subtropical climate influenced by the East Asian monsoon. Summers are wet with high temperatures, high humidity, and a high heat index. Winters are mild and comparatively dry. Guangzhou has a lengthy monsoon season, spanning from April through September. Monthly averages range from 13.6 °C (56.5 °F) in January to 28.6 °C (83.5 °F) in July, while the annual mean is 22.6 °C (72.7 °F). It has a wide water area with lots of rivers and water systems, accounting for 10% of the total land area. In addition, there are 47 different types of minerals and also 820 ore fields in Guangzhou, including 18 large and medium-sized oil deposits.

Administrative Regions
Guangzhou is a city of sub-provincial administrative status in southern China's Guangdong province. It covers a total area of 7343.4 square kilometers, accounting for 4.21% of Guangdong province's land area.
It has direct jurisdiction over eleven districts: Liwan District, Yuexiu District, Haizhu District, Tianhe District, Baiyun District, Huangpu District, Panyu District, Huadu District, Nansha District, Conghua District and Zengcheng District, in which Conghua District is the largest district in Guangzhou (covers an area of nearly 2000 square kilometers).
In 2014, population of Guangzhou reached to 13.08 million (registered residents accounted for 64.4% and urban residents accounted for 85.43%). In the past decade (from the end of 2004 to the end of 2013), the residents increased 3.27 million, up 33.8% over the period; the registered residents increased 0.95 million, up 12.8% over the period.
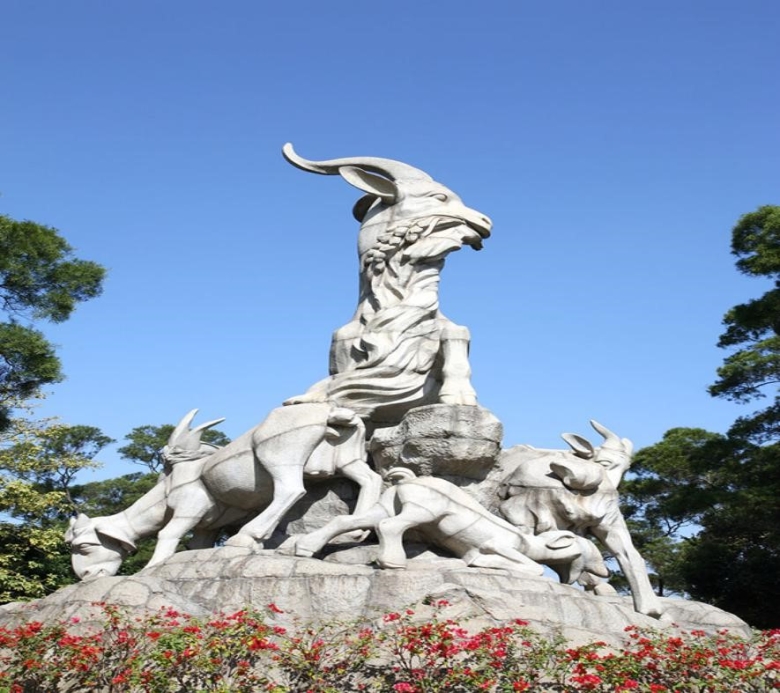
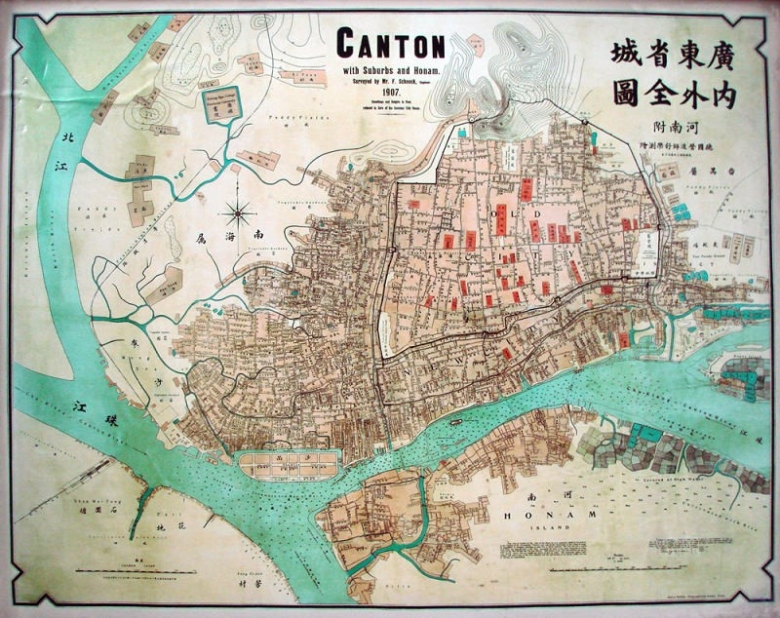
History
Guangzhou, a famous city in South China, was established in 214 BC and it has a long history of more than 2,200 years.
According to historical records, Chu Ting, the earliest name of Guangzhou, was named by Chu state of Zhou Dynasty (11th Century BC - 221BC). When the emperor of Qin Shihuang (259-210 BC) unified the Lingnan region, he established Nanhai prefecture and built Panyu, the present Guangzhou as the capital. In the year of 226, Sun Quan divided Jiaozhou into two parts-Jiaozhou and Guangzhou, so the name of "Guangzhou" was established. Guangzhou became the city it is today when its municipal council was set up in 1921.

This city had always been the political, economic and culture center of South China in history. Nanyue, Nanhan and Nanming dynasties chose Guangzhou as their capital. In addition to this, Guangzhou also was a prosperous city in Qin (221 B.C. to 206 B.C) and Han (206 B.C. to A.D. 220) Dynasties. As the starting point of the Silk Road of the Sea beginning with the Han (206 B.C. to A.D. 220) and Tang (A.D. 618 to A.D.907) Dynasties, Guangzhou grew rapidly and became the largest commercial city and earliest trade port in China by strengthening the foreign trade.
Guangzhou is also the source of modern Chinese revolution, many historic events took place here including the Sanyuanli Struggle against British invaders(1841), the Huanghuagang Uprising against feudalism(1911) and the Guangzhou Uprising which established the Guangzhou Commune(1927). Mr. Sun Yat-sen, a revolutionary forerunner, the first president and founding father of the Republic of China, set up the Huangpu Military Academy, launched a revolutionary movement in Guangzhou and constituted the political parties three times. Then, Guangzhou was occupied by Japan from 1938 to 1945 and the People's Liberation Army of China took over the city in October 1949.

Since the policy of Chinese Economic Reform and open up adopted in 1978, Guangzhou had made it one of the major beneficiaries under guidance of Deng Xiaoping. Today, Guangzhou is the nerve center of the Pearl River delta economic zone and one of the most economically cities in China.